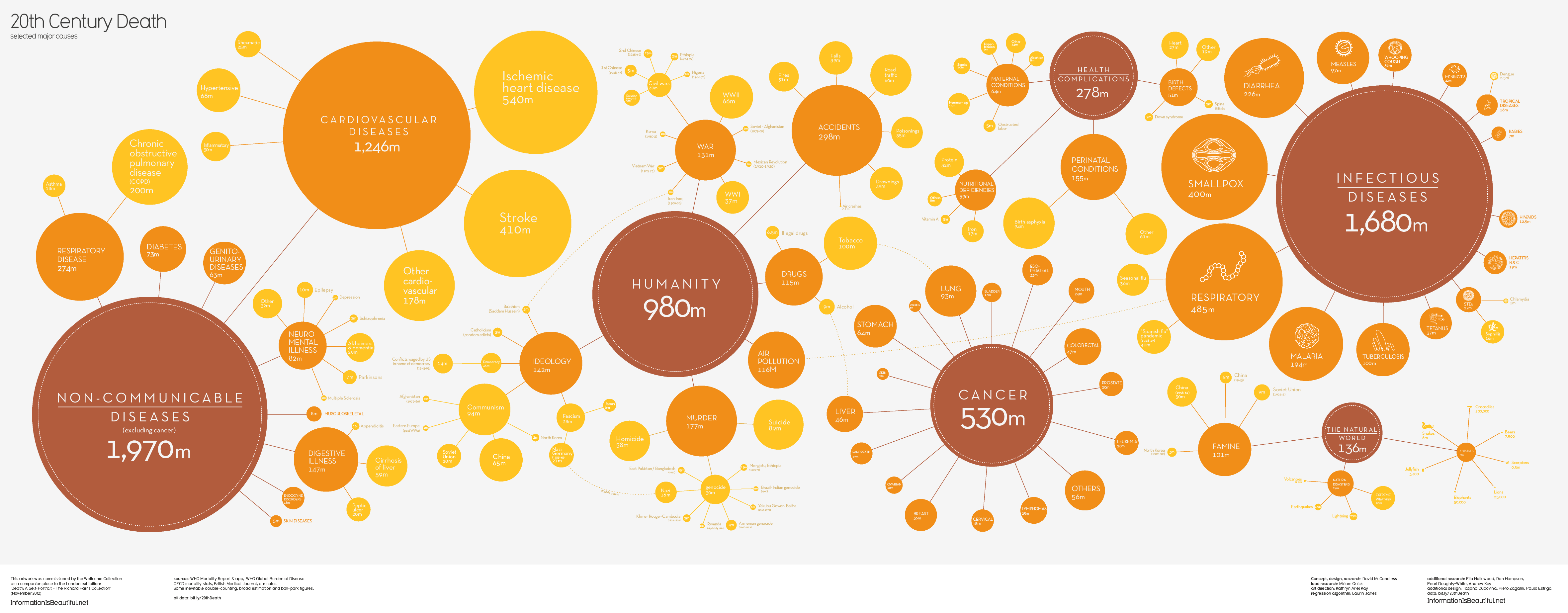
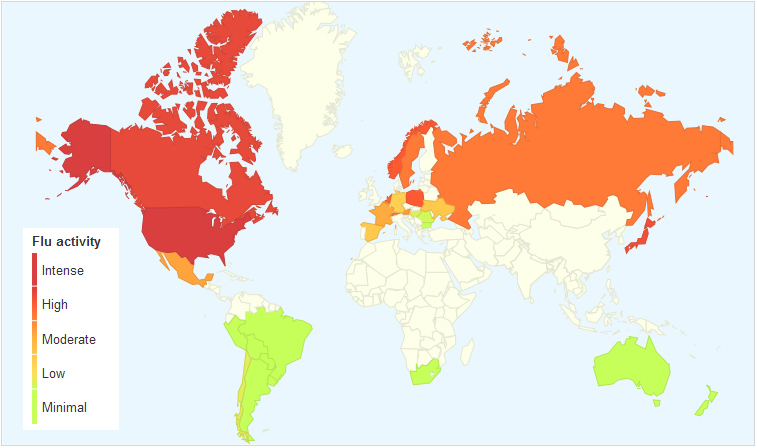
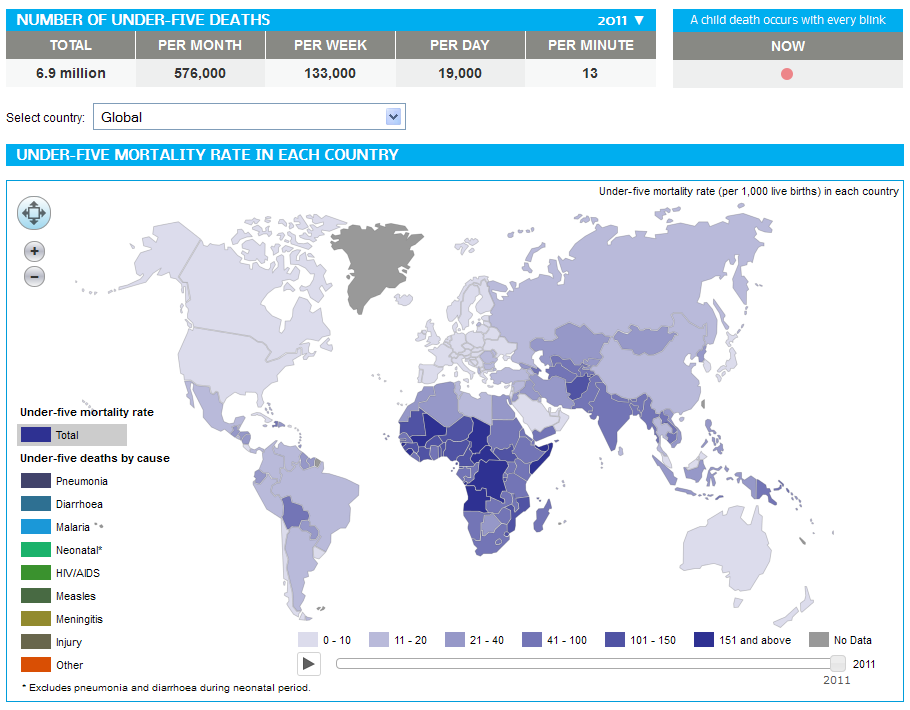
 In 2011, 6.9 million children under five years old died around the globe from different causes ranging from pneumonia, malaria, diarrhea, HIV/AIDS, meningitis, to all kinds of injuries.
In 2011, 6.9 million children under five years old died around the globe from different causes ranging from pneumonia, malaria, diarrhea, HIV/AIDS, meningitis, to all kinds of injuries.
The number of deaths of children under five has decreased by 59% in the last forty years, from 16.9 million back in 1970 to 6.9 million in 2011. That is good news for the world in general; however, there are still regions in the planet where under-five mortality rates have changed hardly at all. That is the case of Africa, where countries with the highest under-five mortality rates include Sierra Leone, Somalia, Mali, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, Guinea-Bissau, and Angola. In other parts of the world, countries with high under-five mortality rates include Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Haiti and Bolivia.
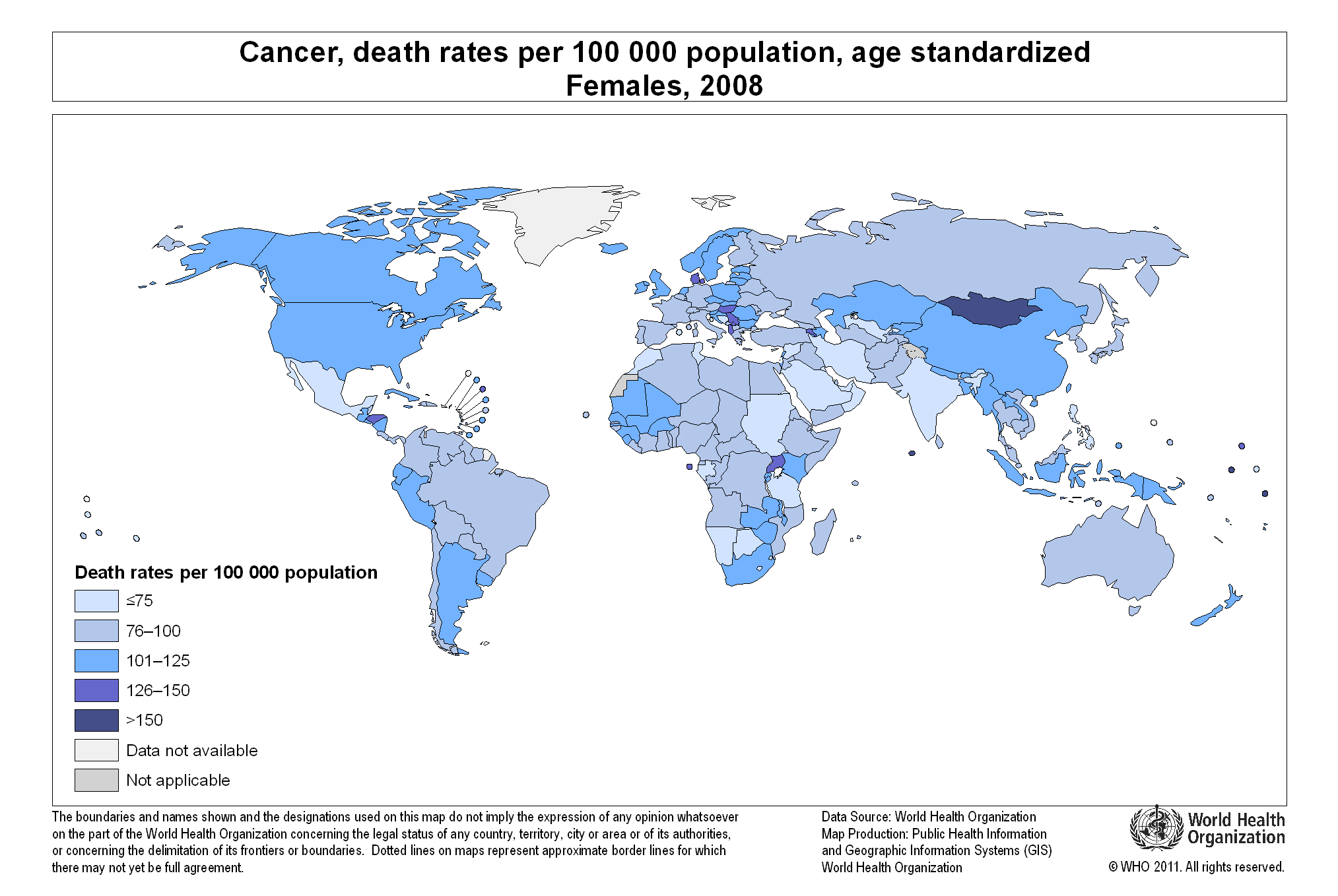
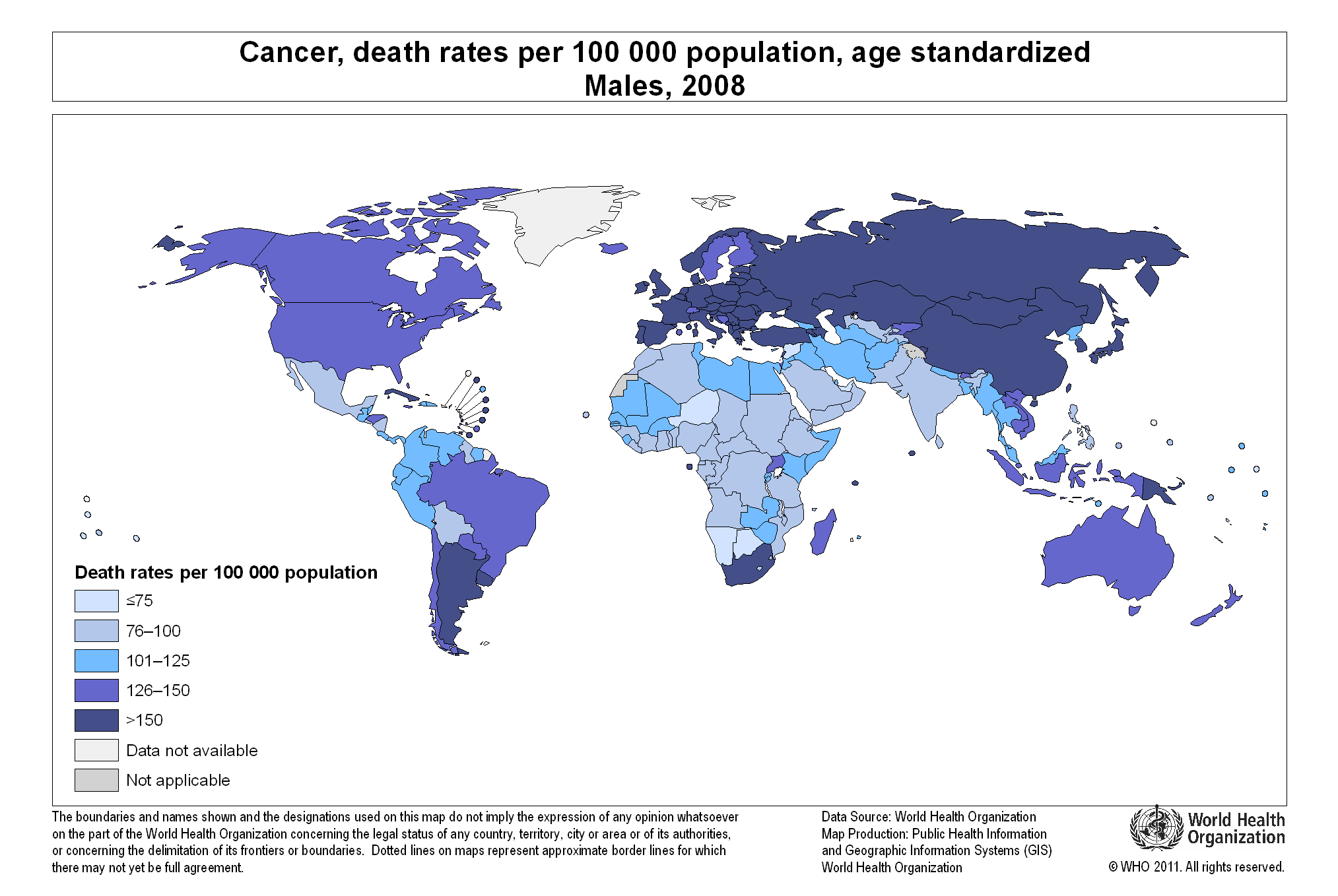
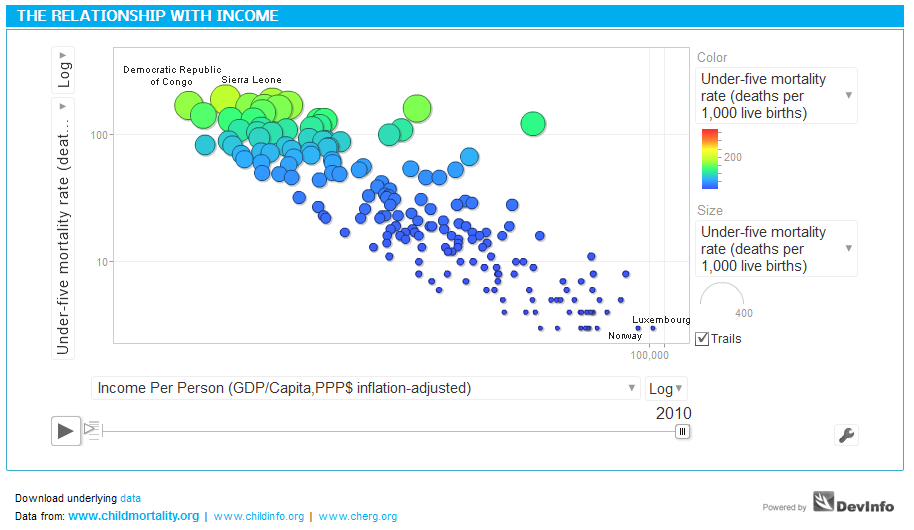 Income is a critical factor influencing under-five mortality rates, as shown in the graph above. The larger the income per capita of a nation, the lower the mortality rate. Such is the case of developed economies like Luxembourg or Norway, in stark contrast with developing countries like Somalia or Sierra Leone, where income per capita is very low.
Income is a critical factor influencing under-five mortality rates, as shown in the graph above. The larger the income per capita of a nation, the lower the mortality rate. Such is the case of developed economies like Luxembourg or Norway, in stark contrast with developing countries like Somalia or Sierra Leone, where income per capita is very low.
Source: Health Intelligence: Under-five Mortality dashboard
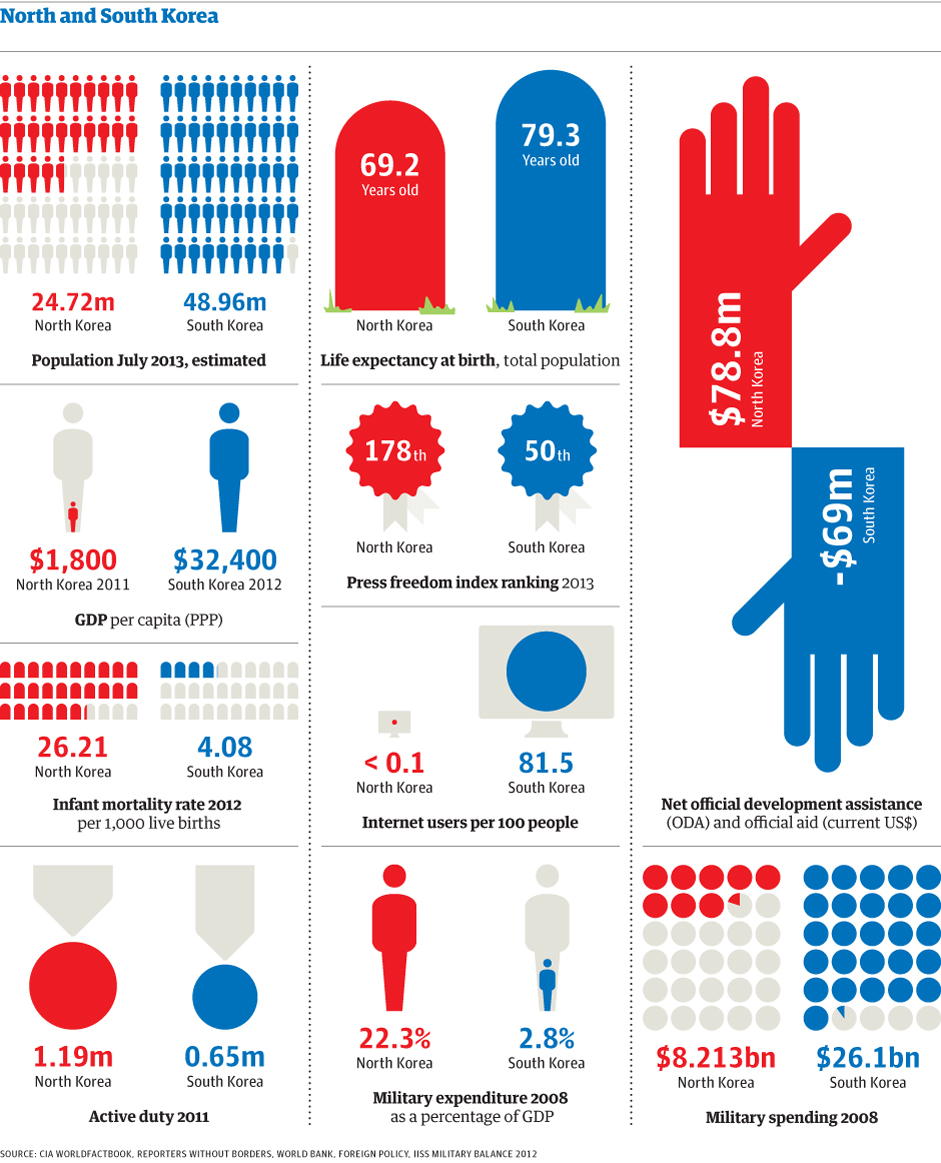 In this visualization created by The Guardian, we can see how North Korea compares to South Korea in terms of population, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), life expectancy, freedom of the press, military spending, internet connectivity, infant mortality, among other indicators.
In this visualization created by The Guardian, we can see how North Korea compares to South Korea in terms of population, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), life expectancy, freedom of the press, military spending, internet connectivity, infant mortality, among other indicators.