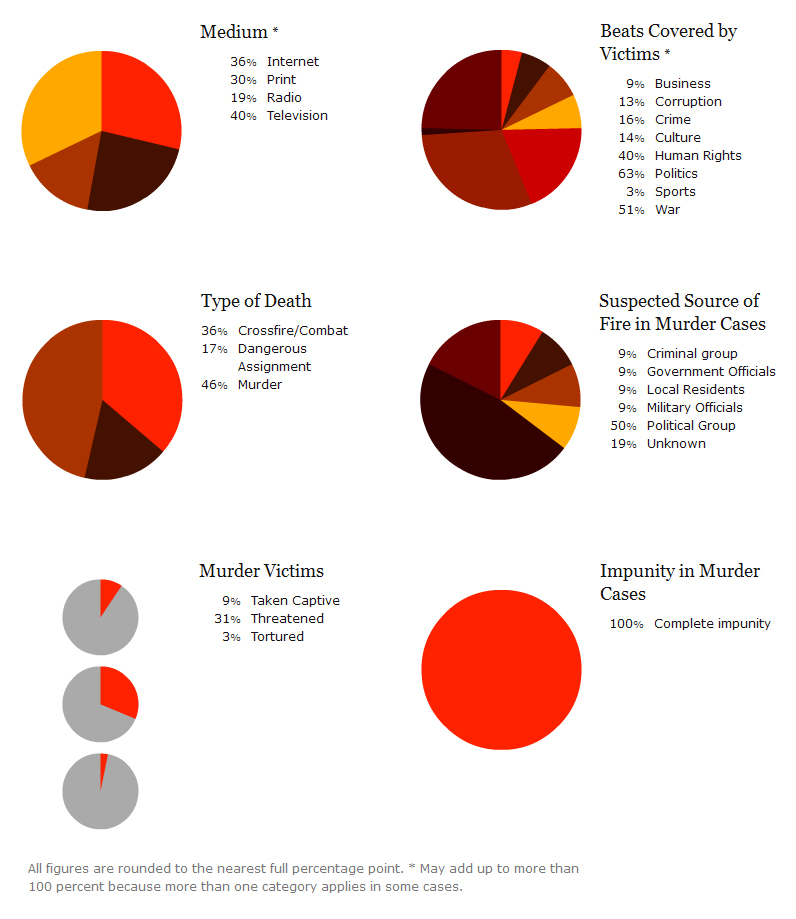
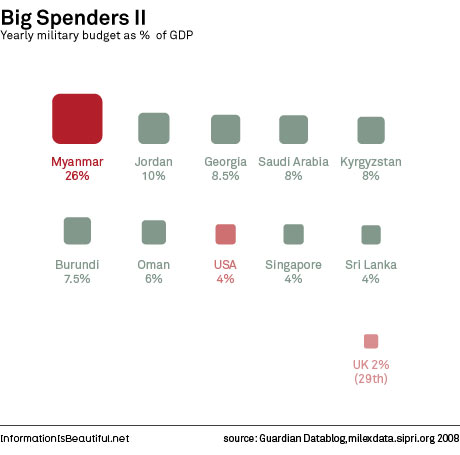
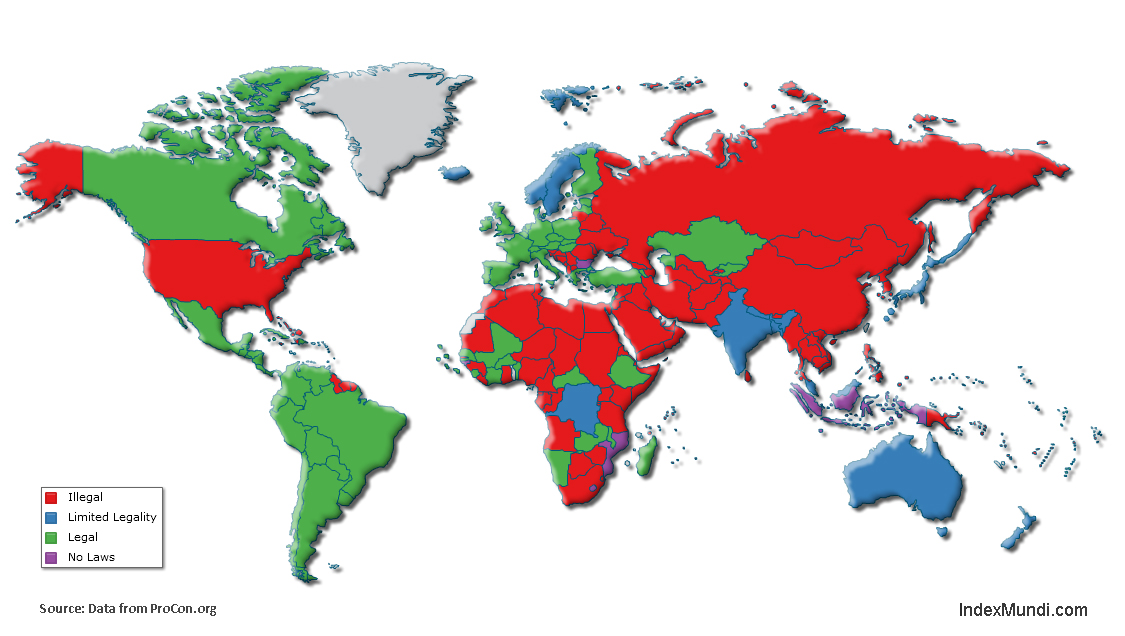
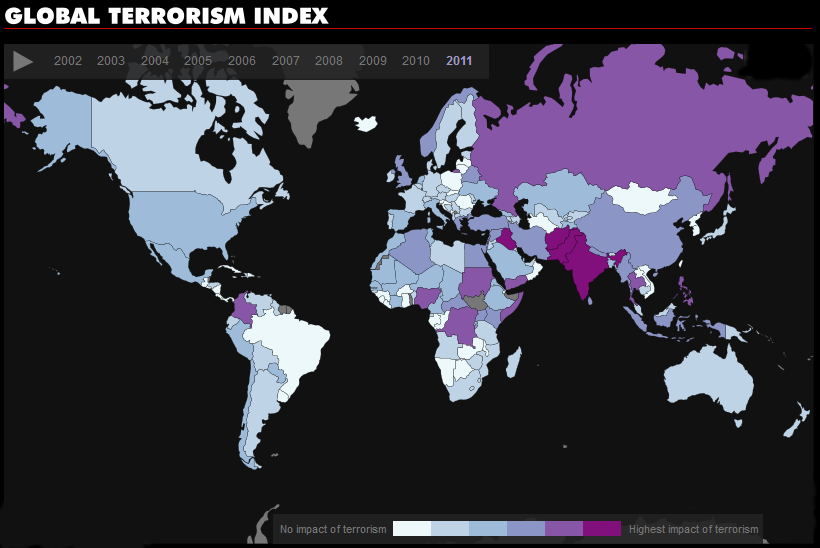
Fossil fuel subsidies are very common in developing nations. Subsidies cover the difference between the price at which fossil fuels are sold inside the country and their actual price in international markets, creating a huge fiscal burden (an estimated $400 billion annually) for the countries that provide them. Developing nations with fossil fuel subsidies include: Venezuela, Argentina, Ecuador, Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Kuwait, Iran, Pakistan, Russia, China, India, Indonesia, etc.
Fossil fuel subsidies are very common in developing nations. Subsidies cover the difference between the price at which fossil fuels are sold inside the country and their actual price in international markets, creating a huge fiscal burden (an estimated $400 billion annually) for the countries that provide them. Developing nations with fossil fuel subsidies include: Venezuela, Argentina, Ecuador, Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Kuwait, Iran, Pakistan, Russia, China, India, Indonesia, etc.
Developed nations also provide subsidies in the form of tax breaks to the oil industry and other measures (estimated at a cost of $45 to $75 billion per year). Nations in this group include many OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) members.
For the interactive map, visit: National Geographic: The Great Energy Challenge: Fossil Fuel Burden on State Coffers