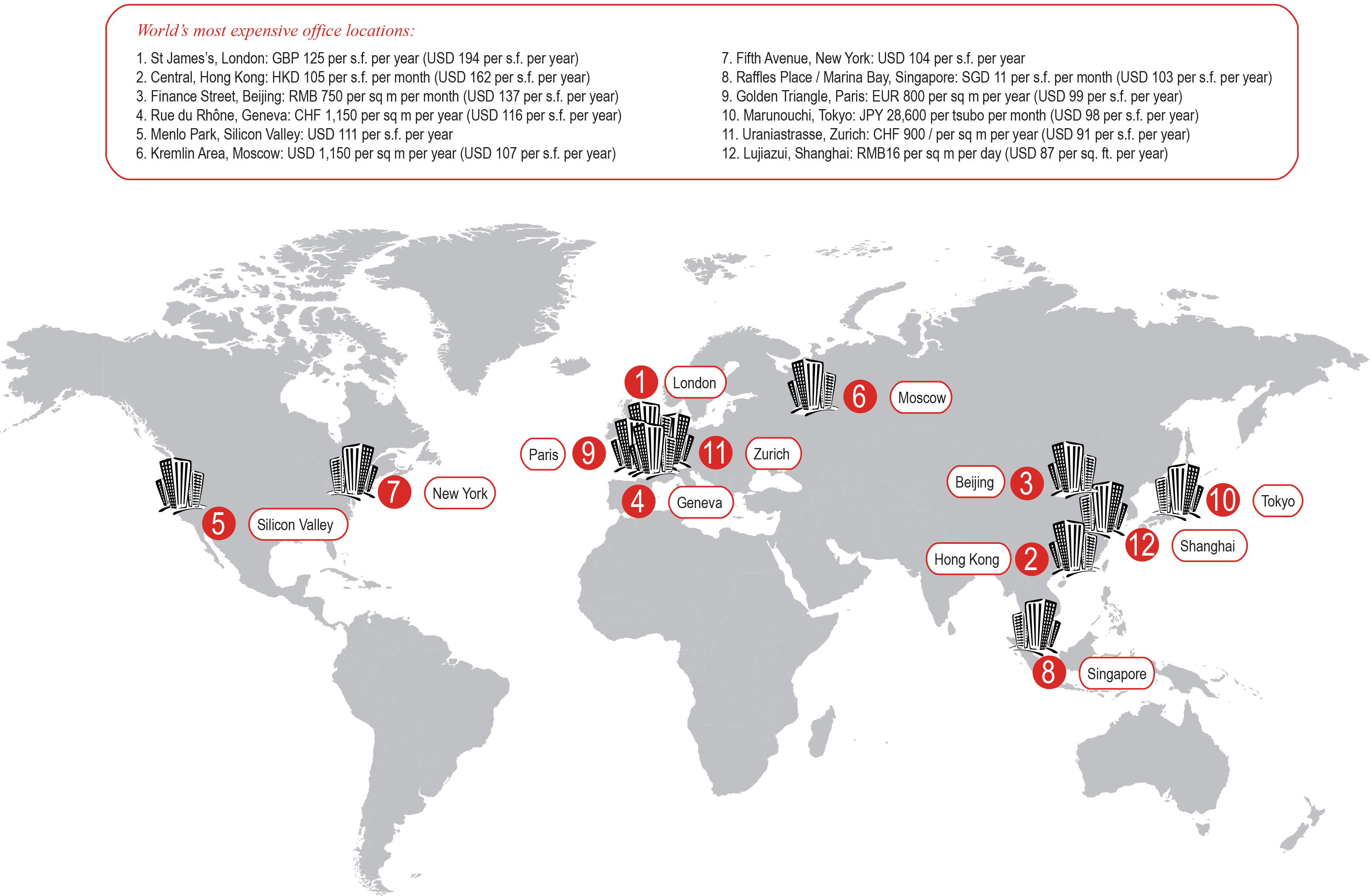
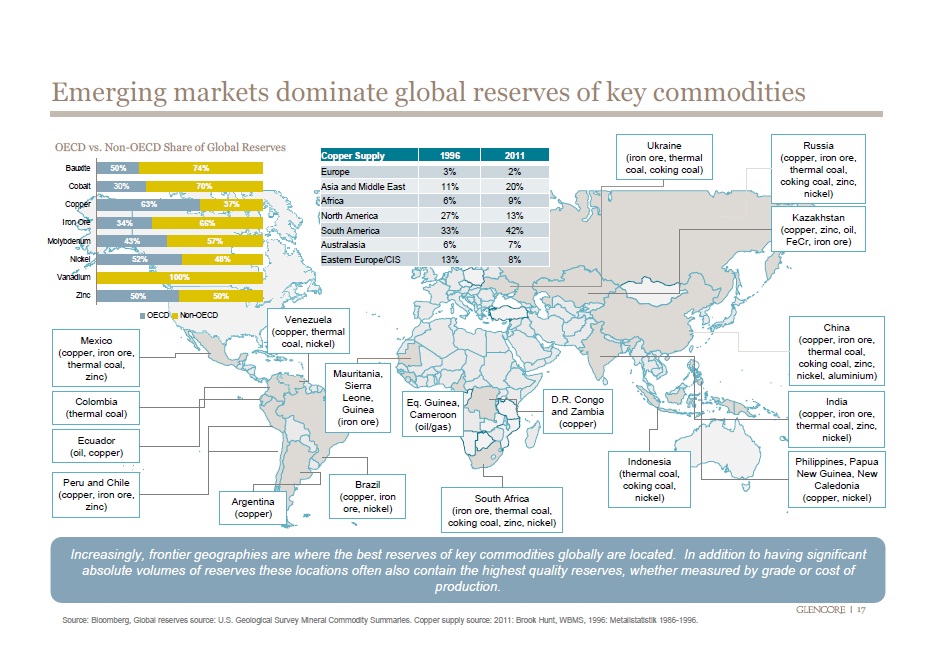
Expensive office locations around the world share similar characteristics: they are located in premier trade and financial centers, they are sites for corporate headquarters, they are located in areas where property availability is scarce and therefore expensive, and they are located close to their most wealthy customers.
As we can see in the map above, the most expensive office spaces are located in Europe, Asia and the United States. London’s St. James area leads as the most expensive location for office space. London is followed by Hong Kong’s Central area, Beijing’s Finance Street, Geneva’s Rue du Rhône, and Silicon Valley’s Menlo Park.
Source: LinkedIn: Paying the Rent: The World’s 12 Most Expensive Office Locations